Navigating through a website is a bit like exploring a city. Internal links are the signposts that guide you from one place to another. Let’s take a closer look at what internal linking is all about and why it’s crucial for your website’s success.
Table of Contents
What is Internal Linking?
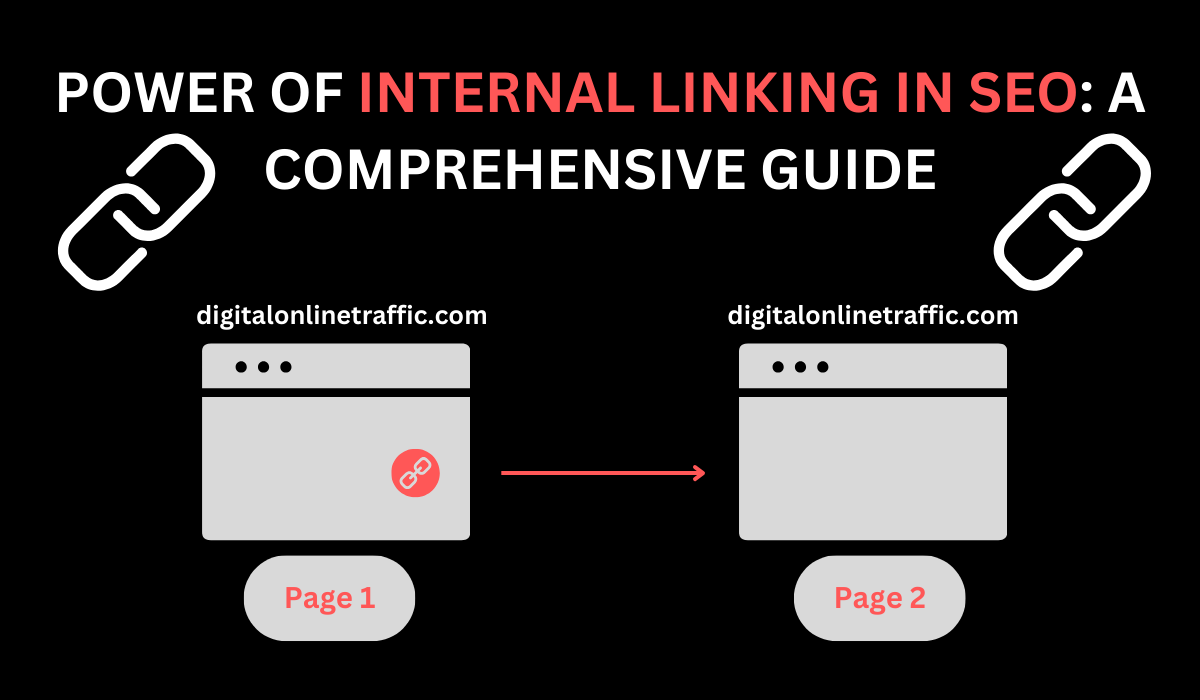
Imagine you’re reading an article on a website and you see a highlighted word or phrase. When you click on it, it takes you to another page on the same website. That’s an internal link! It’s like a secret tunnel that connects different rooms (or pages) of the same house (or website).
Internal Linking Definition:
Simply put, internal linking is like connecting the dots within your website. It involves adding clickable links within your content that direct users to other relevant pages on your site. These links not only aid navigation but also play a crucial role in distributing authority and relevance throughout your website.
Internal Links Example:
For instance, imagine you’re reading an article about different types of flowers on a gardening website. Within that article, you might find links to related topics such as “How to Plant Roses” or “Caring for Orchids.” Clicking on these links takes you to other pages within the same website, providing additional information on the subject.
Types of Internal Linking
1. Contextual Links:
Contextual links are perhaps the most common type of internal linking. These links are embedded within the body of the content, usually within relevant anchor text. They seamlessly integrate into the context of the article or webpage, providing additional resources or directing users to related topics. Contextual links are highly effective because they are naturally integrated into the content, making them more engaging and relevant to the user.
Example:
In an article about healthy eating, the phrase “benefits of antioxidants” could be linked to a separate page on the website that delves deeper into the topic.
2. Navigation Links:
Navigation links are the backbone of website navigation. These links are typically found in menus, sidebars, or footers, providing users with easy access to different sections of the website. Navigation links help users explore various categories, products, or services offered by the website, facilitating smooth navigation and enhancing user experience.
Example:
A website’s main menu may include links to pages such as Home, About Us, Services, Blog, and Contact, allowing users to navigate to different sections of the website with ease.
3. Image Links:
Images can also serve as internal links, allowing users to navigate to other pages within the website by clicking on them. Image links can be particularly effective for enhancing visual appeal and guiding users to relevant content or product pages. However, it’s important to ensure that the alt text of the image provides descriptive information for accessibility and SEO purposes.
Example:
A website showcasing different vacation destinations may include clickable images of each destination, leading users to detailed pages with more information about each location.
4. Footer Links:
Footer links are located at the bottom of a webpage and often include navigational links, contact information, and legal disclaimers. While footer links may not always be as prominent as navigation links, they still play a valuable role in providing users with additional navigation options and reinforcing the website’s structure.
Example:
Footer links may include links to important pages such as Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, Site Map, or Social Media Profiles, allowing users to access essential information regardless of where they are on the website.
5. Breadcrumb Links:
Breadcrumb links are a hierarchical navigation system that displays the user’s current location within the website’s hierarchy. They typically appear near the top of the webpage and provide users with a trail of links representing the path they took to arrive at the current page. Breadcrumb links help users understand the website’s structure and easily navigate back to previous pages.
Example:
A website selling electronics may use breadcrumb links to indicate the user’s path from the homepage to a specific product category, such as Home > Electronics > Laptops > Gaming Laptops.
How Many Internal Links Per Page SEO:
There is no fixed rule for the number of internal links per page in SEO. The key is to maintain a balance between providing helpful navigation and avoiding excessive linking, which can appear spammy to both users and search engines. It’s best to focus on quality over quantity, ensuring that each internal link adds value to the user experience.
Internal Linking Best Practices:
- Use descriptive anchor text that accurately reflects the content of the linked page.
- Ensure that internal links are relevant and contextually appropriate within the content.
- Avoid excessive linking or over-optimization, as this can hurt user experience and SEO.
Is Internal Linking Good for SEO?
Yes, internal linking is extremely beneficial for SEO. It helps search engines discover and index new pages, distributes PageRank throughout the website, and improves the overall crawlability and accessibility of the site.
Internal and External Links in SEO:
Internal links connect pages within the same website, while external links point to pages on other websites. Both types of links are important for SEO, but internal links are particularly valuable for optimizing on-site navigation and distributing link equity.
Benefits of Internal Linking:
- Improves website navigation and the user experience.
- Enhances the crawlability and indexing of web pages by search engines.
- Distributes page rank and authority throughout the website, boosting overall SEO performance.
Internal Linking Strategy:
- Conduct a website audit to identify opportunities for internal linking.
- Prioritize linking to high-value pages that you want to rank higher in search results.
- Monitor internal link performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize SEO.
Why is Internal Linking Important?
Internal linking is important because it facilitates navigation, improves SEO performance, and enhances the user experience. By strategically linking related pages within your website, you can keep visitors engaged, help search engines discover new content, and ultimately drive more organic traffic to your site.
Internal Linking Structure:
A well-structured internal linking system involves organizing your website’s content in a logical hierarchy and interlinking related pages to facilitate navigation and SEO. This includes creating clear pathways for users to explore different sections of the website and ensuring that important pages receive sufficient internal link equity.
Difference Between Internal Link and External Link:
The main difference between internal and external links lies in where they point to. Internal links connect pages within the same website, while external links point to pages on other websites. While both types of links are valuable for SEO, internal links are under your control and can be optimized to enhance on-site navigation and SEO performance.
Conclusion:
Internal linking is a fundamental aspect of SEO that plays a crucial role in optimizing website navigation, improving the user experience, and enhancing SEO performance. By understanding the importance of internal linking and implementing best practices, you can create a well-structured website that is both user-friendly and search engine-friendly. So, don’t underestimate the power of internal links—embrace them as a vital component of your SEO strategy and watch your website flourish!